Research
Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China 03/2019–present
Supervised by Prof. Chongxuan Liu (Chair Professor)
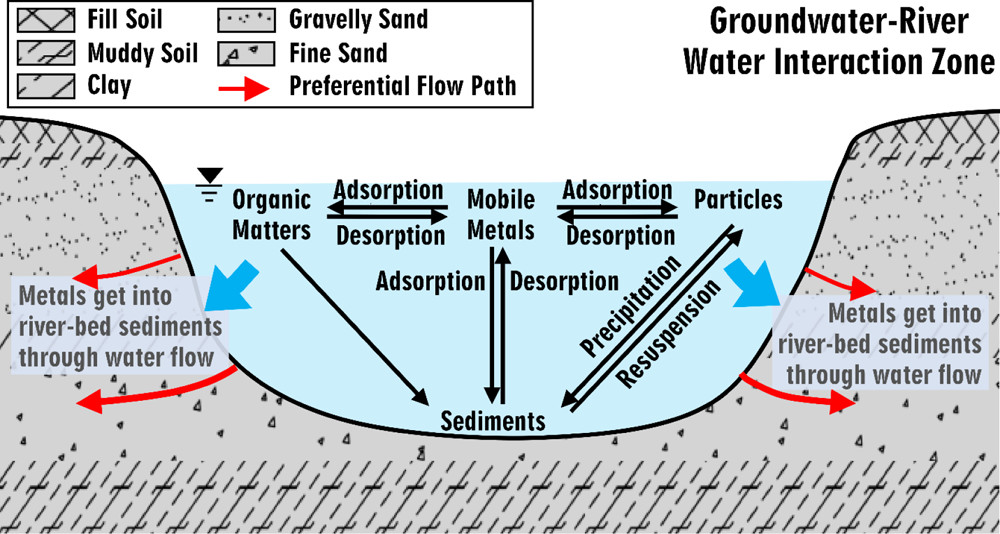
- The dynamics of iron and pollutant hydrobiogeochemistry in the hyporheic zone:
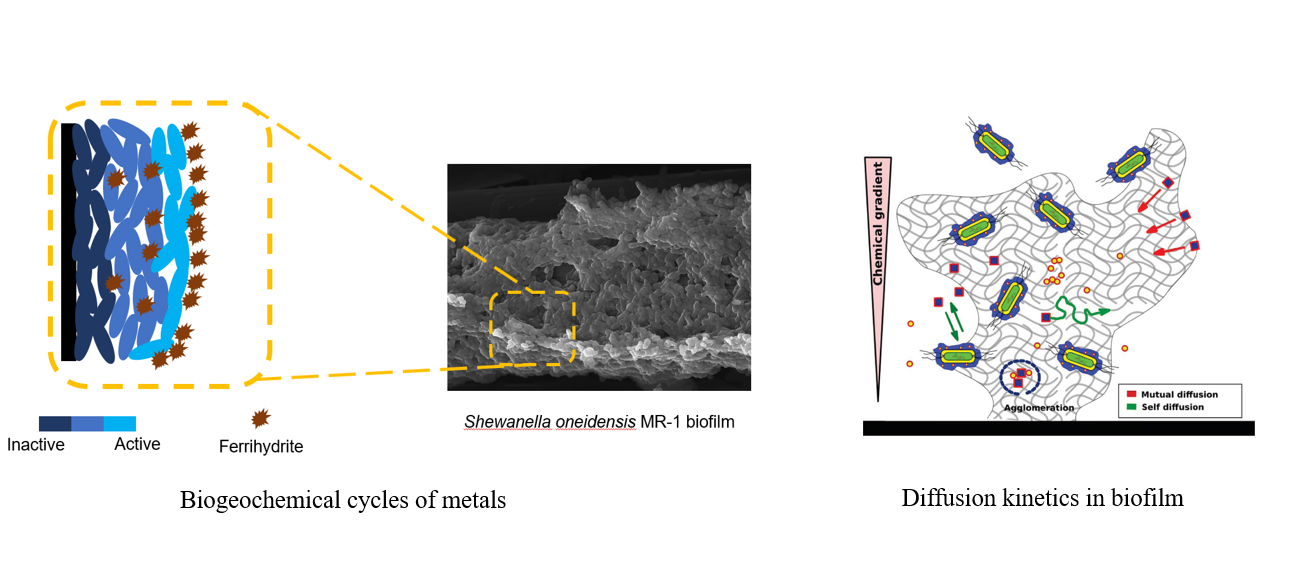
- Dynamic analysis of biofilm reduction kinetics of ferrihydrite. A comprehensive biofilm reduction model was developed and explain the rate differences caused by the biofilm thickness in iron reduction and transformation.
- Investigating hydrodynamics and hydrochemical effects on biofilm function in iron biogeochemical cycles. The research focuses on the interaction between iron bioreduction with biofilm and transport in the water-sediment interface. A reactive transport model which coupled reduction kinetics and detachment kinetics was developed.
- Upscaling iron bioreduction rates with ML approaches.
- Reactive transport experiments and modeling of antibiotics in porous media. The research highlights the impact of flow interruption on adsorption and transport in porous media.
- The co-evolution of microbial biofilm function and hydrobiogeochemical processes:
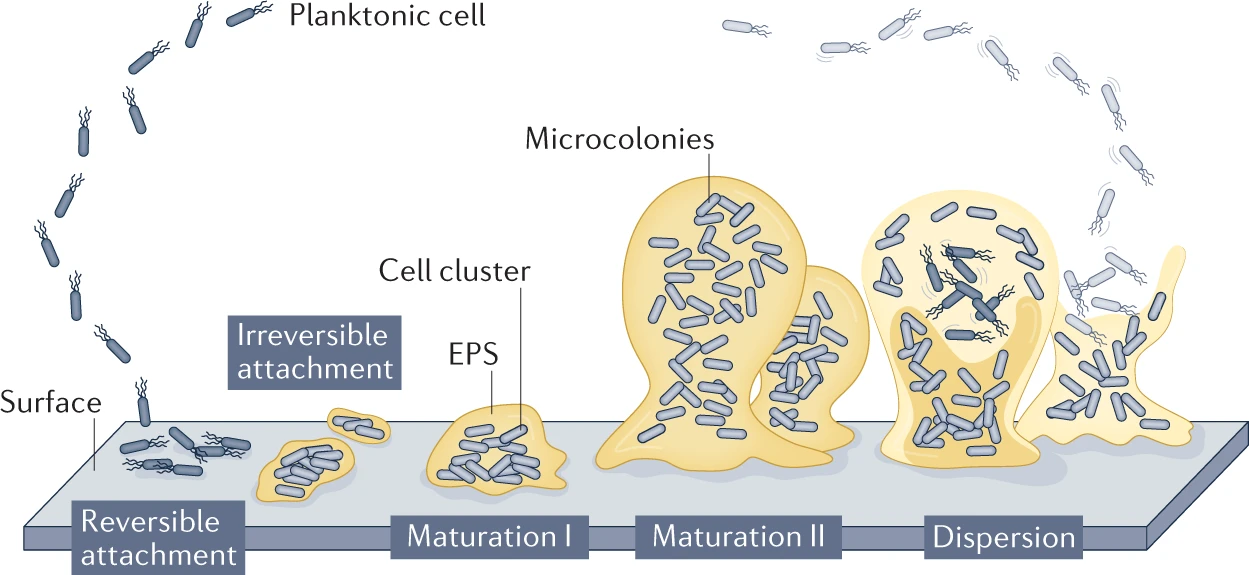
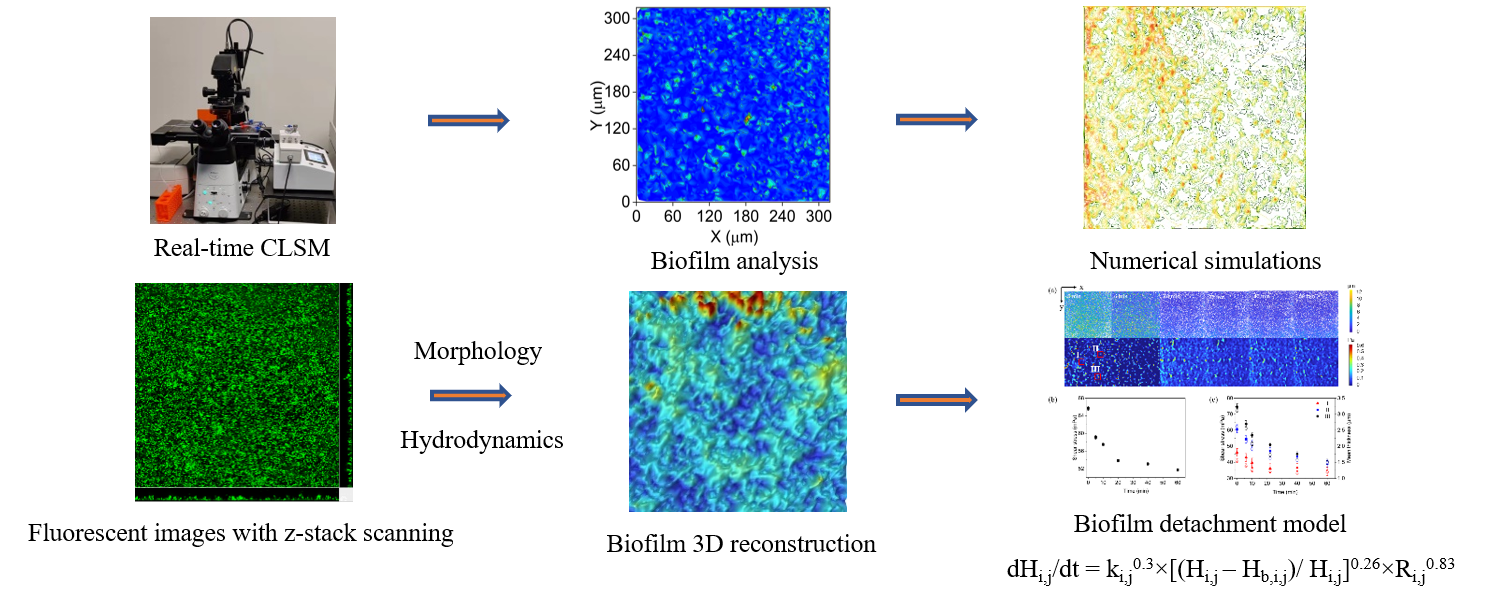
- Investigating the influence of hydrodynamics on biofilm 3D microstructures and biofilm response to complex dynamic flows. A universal biofilm detachment model was established in this study.
- Utilizing CFD and ML approaches to unravel the mechanisms of biofilm detachment under complex environmental factors.
- Molecular-scale interfacial adsorption for environmental contaminant removal:
- Gaining microscopic insights into the adsorption of antibiotics with clay minerals. The research employed macro-scale adsorption experiments and micro-scale molecular dynamics simulations to unravel the surface mechanisms.
Reference:
- Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8, 3367–3373.
- Nat Rev Microbiol 20, 608–620 (2022).
